Actuality
Nowadays, financial institutions are facing an ever-increasing cyber-threat landscape, these institutions have always been in the crosshairs of cyber-attackers due to the financial assets they manage but, in the actuality, the cyber-attacks performed by criminal groups are more extreme. Therefore, in order to avoid the possibility of disrupting crucial financial services by means of crippling their cyber security, a need to evolve the mechanisms used to ensure the cyber resilience of these institutions have arisen. This have led to the urge of approaching improvements of the cyber resilience for financial institutions, resulting in multiple procedures that have been published by different organisms.
In order to being able to improve the cyber resilience of an institution, it is necessary to perform an analysis of the actual state, this can be done with:
- The implementation of a methodology whose main function is to allows the organization to anticipate and adapt to cyber threats and to quickly identify, respond to and recover from potential cyber-attacks.
- The studio of the infrastructure in order to identify possible vulnerabilities that could be used by an attacker, this way, it is possible to evaluate the institution response to various situations, the resistance of penetration tests to assess, systems...
- Testing in a real scenario which allows the institution to evaluate the cyber resilience of their infrastructure in a practical way, this type of testing need to be carried by a Red Team in order to test the entire infrastructure by simulating the tactics, techniques and procedures that real attackers would follow, as a result, it is possible to obtain information about the response and recovery time to threats.
To facilitate these conditions, different test frameworks have been developed to improve the cyber resilience of institutions by providing a series of methodologies and steps to be followed. Some of the current test frameworks are AASE from Singapore, CBEST from the United Kingdom, FEER from Saudi Arabi, iCAST from Hong Kong SAR or TIBER-EU from Europe.
Essentials teams in a cyber security testing framework.
There are different approaches of cyber security testing frameworks, each one of them is different but they have in common the main teams that need to take part, these are:
White Team
- Should be members of the institution that is going to be tested.
- Is responsible of the planification and the management of the tests.
- During the tests they are going to be in contact with the different teams.
- Must have a broad knowledge of the functions fulfilled by the institutions and the operations that are performed.
- The members must be able to take critical decision in the institution in case of being necessary for any of the tests.
- The size of the team must be small in order to maintain the confidentiality of the test inside the institution.
Red Team
- Is the team that performs the test in order to simulate the tactics, techniques and procedures of real attackers.
- Must attack the different threats identified.
- The objective of the different test must be in the scope, including members, technologies and procedures of the institution.
- Must be in coordination with the White Team to ensure that the necessary precautions are taken.
Blue Team
- Is in charge of preventing, identifying and responding against the attacks that target the institution.
- Must not know that the institution is being tested by a Red Team, this way, the results obtained will be as close as possible to a real attack scenario.
Common steps of a cyber security testing framework
Each cyber security testing framework will have its own steps or phases but, in some way, they all follow something similar to the steps includes below:
- Definition of the target scope within the institution that is going to be tested.
- Establish the risk that will be exposed in the institution during the tests.
- Choice of the teams that are going to identify threats in the institution and to perform the testing.
- Reconnaissance of the institution infrastructure.
- Perform of the test by the Red Team.
- Analyze the results of the test performed.
- Propose of a plan to mitigate the errors identified.
European testing framework TIBER-EU
The European testing framework TIBER-EU has as its objectives the improvement of the cyber resilience of the financial institutions (but it is also applicable to any other critical sector) and to provide assurance of the cyber resilience capabilities of the entities tested thanks to the supervision of the TIBER-EU authorities.
The framework has been developed in order to perform the test in the European Union but it has enough flexibility to be adapted to other legislations, due to that, it is possible to carry out the tests in multinationals that are distributed among different countries and, in order to be able to promote mutual recognition between the authorities of different countries, it establishes a protocol for collaboration, analysis and sharing of the results, this way, its enables a cross-border recognition of TIBER test.
As the testing framework has been designed to be adopted by the authorities of different nations, it makes possible the supervision of the entities improving the financial stability, these authorities should be in charge of considering which entities should carry out the tests.
In addition to the essential roles defined before, the TIBER-EU add three extra roles, these roles are described below:
Threat Intelligence provider: is the team in charge of providing Threat Intelligence of the institution using multiple sources of intelligence including OSINT, HUMINT and geopolitical knowledge.
TIBER Cyber Team: the function of this team is to provide support to the White Team, supervise the test and provide support for the supervisors in the case that these are not part of the TIBER Cyber Team.
Relevant governmental intelligence agencies: this role is optional and could be used to provide feedback of the different reports generated in the test.
In relation to the steps that need to be carried in the framework, it is composed of three obligatory phases and one optional phase, these phases can be overlapped to provide feedback between phases and assure the best results. The different phases are described below:
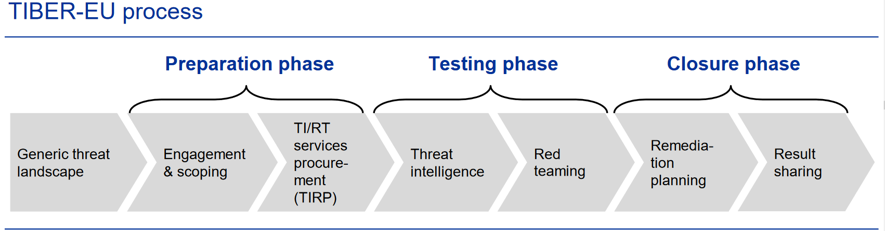
Generic Threat landscape: This is the optional phase, it involves a generic assessment of the threat landscape from the national financial sector, analyzing the specific functions of the various entities, identifying the relevant threats and the tactics, techniques and procedures to which these entities are exposed. This phase aims to link the threats to the sectors institutions in order to be able to use this information for the development of the attack scenarios. This phase should be updated if new threats, tactics, techniques or procedures that pose a risk are identified.
Preparation phase: during this phase, the engagement for the test is formally launched, the teams are established, the scope is determined, approved by the institution and validated by the authorities. (4-6 weeks).
Testing phase: in this phase, the Threat Intelligence provider and the Red Team works closely, the function of the Threat Intelligence provider is to prepare a Targeted Threat Intelligence Report of the institution, this report contains the threat scenarios that have been identified and also provides useful information of the entity. The information from the Threat intelligence provided is used by the Red Team to develop the attack scenarios, obtain intelligence of the critical system, people and processes of the institution and perform the tests. In the event that the Red Team performs a series of attacks on a particular system and it is shown that it is adequately protected, it could be possible to meet with the White Team and ask for a step-up in order to be able to continue the test inside the system. (Threat Intelligence provider 5 weeks | Red Team 10-12 weeks).
Closure phase: is the ending phase of the framework, the Red Team will provide the results of the test that will be a practical assessment of the entitys protection, detection and response capabilities. This information needs to be reviewed and discussed to prepare a remediation plan and the key findings will be shared with the authorities. Finally, this phase end with the approval to close the test. (4 weeks).
Some of the main points to adopt the TIBER-EU framework is how well-defined are the procedures that need to be followed, the requirements that need to accomplish the different teams and the separation from Threat Intelligence provider and Red Team, this distinction makes possible to choose the best team for each job, one team trained to collect and analyze information and one team to perform the attacks.
In order to be eligible to work as a Red Team or a Threat Intelligence provider in a TIBER-EU test there is a well-defined list of requisites that need to be accomplished. From our point of view, the most important ones are that it is required to have references from previous assignments related to the job in question, a manager with huge experience and references and team members that have enough experience and are multi-disciplinary. For example, for a Red Team it is required to know penetration testing, exploit development, physical penetration… and the Threat Intelligence provider must have members experts in HUMINT, OSINT… Being as a requisite that this experience is proven with qualifications and certifications.
Differences between frameworks.
One of the characteristics that need to be compared between different frameworks like AASE, CBEST, FEER, iCAST and TIBER-EU, is the targets of the framework, most of these frameworks are oriented to the financial institutions of the countries where the framework have been developed with the exception of TIBER-EU, for this one, one of the mains objective is the possibility of making it flexible, being able to be adapted to different countries and due to that, it is also oriented for multinational financial institutions.
In regard with the teams, all of these frameworks imply that the test is performed by external teams except the AASE and the iCAST that allows that the teams are from the same organization which could lead to the identification of less vulnerability due to not having a third-party point of view. Also, regarding to the accreditations, only the CBEST and FEER requires that the teams are certified, other like the TIBER-EU offer the possibility to certify the teams but do not oblige it. Finally, in relation with the Threat intelligence provider and Red Team, just the TIBER-EU and CBEST demand the separation, this mean that this task need to be performed by two different teams, this is an important requirement because it imply the use of specific teams specialized in each function.
In conclusion, the CBEST is a very good frameworks in means of cyber security but it is oriented to the UK, missing the methods implemented by TIBER-EU to make it international, due to that, one of the best frameworks to adopt would be TIBER-EU with the use of teams that have been certificated, making it able to perform the test with well qualified teams and across multiple nations.
If your company wants to carry out a cyber security test in your infrastructure do not hesitate to contact us, our Red Team is composed of experts in continuous training that are up to date on the current threats and tactics used by attackers, allowing them to replicate real-life attacks following a penetration testing methodology.












