5G technology has been, and is considered by the European Commission, as a strategic and competitive opportunity, as it enables industrial transformations through wireless broadband services at gigabit speeds, the support of new types of applications connecting objects and devices (IoT) and the versatility of networks through software virtualisation. This set of features, among others, will enable innovative business models in many sectors (e.g. transport, healthcare, manufacturing, logistics, energy, media and entertainment).
The interconnection of 5G with other networks, the transnational nature of cyber-attacks and the foreseeable use of 5G for essential functions in the economy and in society, means that the potential impact on critical infrastructures in the event of a security incident is potentially high. We should not forget the multiplicity of access points, as well as the huge amount of information transmission that is expected with the use of this new technology.
The interconnection of 5G with other networks, the transnational nature of cyber-attacks and the foreseeable use of 5G for essential functions in the economy and in society, means that the potential impact on critical infrastructures in the event of a security incident is potentially high. We should not forget the multiplicity of access points, as well as the huge amount of information transmission that is expected with the use of this new technology.
First steps of 5G in Europe
As early as 2016, the European Commission launched an action plan that envisaged the adoption of this technology for the period 2020-2025 through the "Shaping Europe Digital Future" programme. On 29 January 2020, the European "toolbox" was published, identifying a identifying a set of measures that can be adopted by Member States to mitigate the main risks to the cybersecurity of 5G networks and to guide Member States in the selection of measures to be prioritised in risk mitigation plans at state and EU level, so as to ensure an adequate level of cybersecurity of 5G networks at European level and coordinated criteria between Member States, including Spain.
All these research, dispositions and recommendations have led to the creation in Spain of a "Borrador de Anteproyecto de Ley sobre requisitos para garantizar la seguridad de las redes y servicios de comunicaciones electrónicas de quinta generación". This Draft Bill is the legislative adaptation that has been carried out in Spain based on the different European provisions relating to the certification and requirements that will be imposed for the deployment of 5G and which are referred to in the previous paragraph. It should be noted that each Member State will decide how to apply the implementation of 5G in its legislation, always on the basis of European recommendations. In this article we will extract the most relevant aspects of cybersecurity certification according to Spanish legislation.
A new and decisive stakeholder comes into the picture, the suppliers.
The proper functioning of 5G networks will depend heavily on IT systems and services provided by hardware, software and 5G service providers (called suppliers), which are external, but not unrelated to the incumbent telecommunications operators. Therefore, a high dependency on these suppliers is created, which logically increases the level of risk.
Telecommunications operators should review the security practices of their suppliers that may have an impact on the products and services they provide and should manage the risks arising from the performance of their suppliers. Operators are therefore obliged to require compliance with safety standards, from product design to commissioning, as well as control of their own supply chain.
Is certification in 5G networks and services mandator in Spain?
This is a difficult question to answer and one that should be considered at two levels. At the private company level, in principle, it is not mandatory unless the contracting company requires it, although it is highly recommended. At the level of access to public tenders, the perspective changes, as indicated in Article 15 of the Draft Bill: “The Government may make the use of external equipment, software or services in the management of 5G networks subject to prior certification in accordance with (EU) 200119/881 of the European Parliament". The certifications covered by this regulation are those included in the Cybersecurity Act and covered by the URWP, as we explained a few months ago in our blog "Cybersecurity certification in Europe - 2 years of the Cybersecurity Act"..
Therefore, it is understood that the Administration may, if it deems it appropriate, require the possession of a cybersecurity certification derived from a European certification scheme included in Regulation (EU) 2019/881. In addition, the condition of being able to exclude suppliers who do not have the required certifications, depending on the subject matter of the contract, is retained.
This perspective imposes an obligation on bidders to provide proof of the applicable certification, imposes an obligation on bidders to provide proof of the applicable certification, otherwise they cannot be awarded the contract. Our recommendation is, whenever possible, to be proactive and prepared for such cases by starting the certification process before being unable to apply for certain tenders.
Scope and objectives of the new 5G scheme
In view of the imminent deployment of 5G technology in Europe in the coming years, the European Union included in the URWP the creation of a specific cybersecurity scheme for this technology. The objective of the creation of this new scheme is none other than to improve the 5G cybersecurity framework and to ensure that the deployment of 5G in the European Union is carried out in a secure manner.
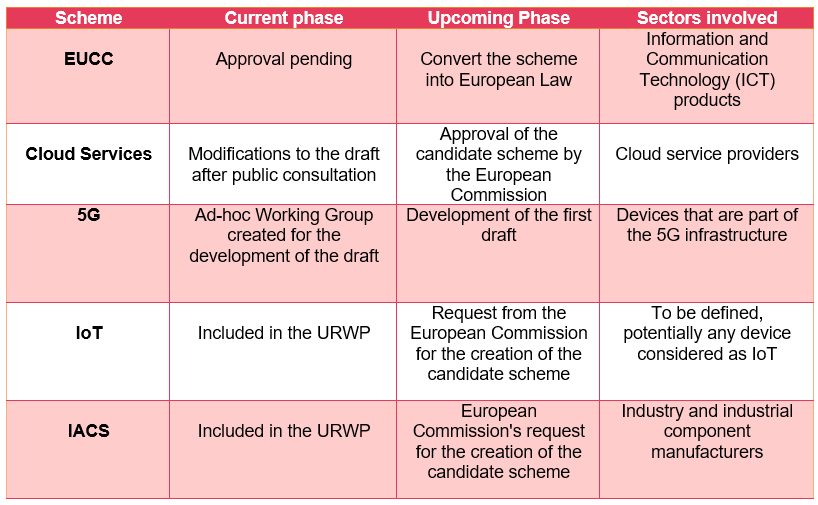
After the creation of an AHWG (Ad Hoc Working Group) by ENISA, following a request by the European Commission, we are currently in the phase of creating the first draft of the candidate scheme for 5G networks (EU 5G scheme). This scheme will focus its scope on the following use cases for 5G cyber security certification:
How can we help you with 5G cybersecurity certification?
We are a laboratory with a strong specialization in evaluating ICT products and services under different standards, some of them as recognized as LINCE, Common Criteria o ETSI EN 303 645.
Furthermore, , we have experience in the creation of European schemes, being an active part of the AHWG for the creation of the EUCC, a project that is in its final phase. Finally, we are members of the SCCG (Stakeholder Cybersecurity Certification Group) advising the European Commission on cybersecurity matters.
Tell us what you need and we will help you!












